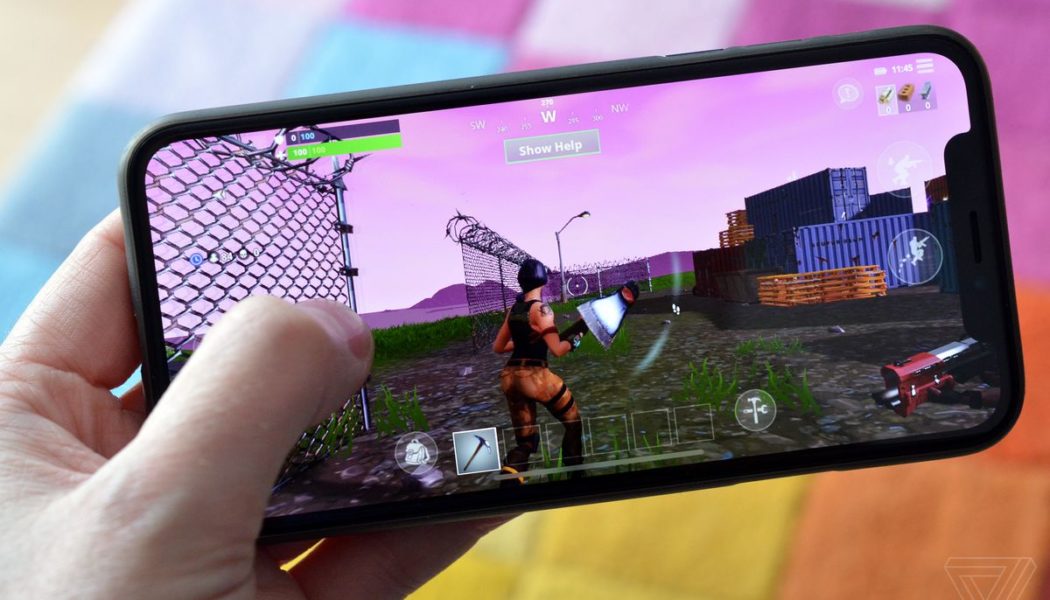
Something keeps coming up at the Epic v. Apple trial as a potential alternative for getting Fortnite on the iPhone: web apps. It’s an intriguing idea, as web apps are able to do surprisingly complex things: just look at a Chromebook or even game streaming services on the iPhone. But potential is far from reality, because the ability for web apps to look, feel, and perform as well as native apps on iOS is severely limited.
These web apps aren’t the preferred way for consumers or developers to use or create apps on the iPhone, either. But Apple has forced companies like Microsoft and Nvidia to use web apps, instead of native ones available in the App Store.
Though the term itself hasn’t really come up explicitly, what’s being discussed are Progressive Web Apps, or PWAs. If you’re unfamiliar, think of them as slightly more advanced web apps that you can “install” directly from your web browser on to your home screen. Google has been pushing the idea (though support for PWAs on its own platforms is a little mixed), and some companies like Microsoft and Twitter have wholeheartedly embraced PWAs.
Not Apple, though. There are a variety of reasons for that — ranging from genuine concern about giving web pages too much access to device hardware to the simple fact that even Apple can’t do everything. There’s also the suspicion that Apple is deliberately dragging its feet on support for features that make PWAs better as a way to drive developers to its App Store instead.
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/10437351/fortniteiphonex.JPG)
But the App Store has restrictions that aren’t tenable for some developers. That’s the whole crux of this trial for Epic, after all. On the stand, a Microsoft executive detailed the company’s struggles to get its xCloud game streaming service onto iOS. Lori Wright, VP of Xbox business development at Microsoft, revealed the company spent around four months talking to Apple to try and get xCloud launched as a native app. Apple seemed, initially open to the idea of letting Microsoft use the same model as Netflix or Audible. But Apple changed its mind and forced Microsoft, Nvidia, and others to list cloud games as separate apps.
Submitting Xbox games one-by-one was simply a nonstarter for Microsoft, so it resorted to making a web app. In addition to the technical hurdles a web app involves, it also introduces a discoverability issue. Users simply aren’t used to installing apps from the web on their iPhones. Apple has effectively trained everybody that if they want an app, they go to the App Store.
Wright essentially admitted that the only reason Microsoft is releasing Xbox Cloud Gaming (xCloud) as a web app is because Apple’s terms on the App Store are too onerous. “People don’t play games through the browser on iPhone,” said Wright, but “it was our only outcome in order to reach mobile users on iOS.”
Even the judge in the case seemed confused by Apple’s rule, which says that services that stream movies can offer them all in a single app but services that stream games have to separate each game for individual listing and review. “I can use Netflix with a native app and I can see lots of different movies or TV shows or whatever. Is it that you didn’t want to use a subscription model?” Judge Yvonne Gonzalez Rogers asked at one point.
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/16334298/microsoft_xcloud_e3_2019_1.jpg)
But back to those technical hurdles: they’re tall, numerous, and can be blamed both on the nature of web apps and Apple’s own decisions. Safari on the iPhone only recently became capable of supporting a service like Xbox Cloud Gaming via specific controller support. Until then, that sort of thing was on the list of features Apple was reticent to include in Safari. There are legitimate reasons to block things like Bluetooth access from web apps, including fingerprinting for tracking, but it was getting harder to justify and Apple needed some kind of escape valve as pressure mounted to support cloud gaming services.
Google software engineer Alex Russell recently published a very comprehensive list of all the features that Safari on iOS doesn’t support yet — and it’s a long list. For PWAs to truly be a viable alternative to App Store apps, there are at least a few of these features that need to be enabled. The inability to send push notifications via a web app, for example, is particularly galling as it’s already possible on Safari on macOS. An app that can’t send notifications is simply not competitive with an app that can.
Grant is touching on some more of the benefits to native versus web apps; push notifications and ARKit both come up. The former is another example of Apple letting native apps reduce friction points — Epic needs to convince the judge these smaller features are meaningful.
— Adi Robertson (@thedextriarchy) May 5, 2021
As Russell notes, his “interests and biases are plain” as a Google engineer. But it doesn’t change the fact that there are many things that a PWA cannot do on the iPhone that a developer like Epic would need to support Fortnite as a web app.
“Native [iPhone] apps would have access to a far wider range of APIs than web apps,” explained Andrew Grant, engineering fellow at Epic Games, during the trial. “Access to things like push notifications, to Siri, to health data, and augmented reality features” are also limited to native apps, said Grant. Web apps also have to be far smaller than native apps, and are capped at about 50MB in size.
Plus, from a simple performance perspective, web apps have more overhead than native apps — and lack access to Apple APIs that can speed up games like Fortnite.
In fact, this was a sticking point for a lot of the questioning of an Nvidia employee. Nvidia, like Microsoft, has been trying to get its GeForce Now cloud gaming service into the App Store, but has faced the same restrictions that Microsoft is struggling with. Nvidia director of product management Aashish Patel spent a lot of time answering questions around latency in a browser and the benefits of using native apps.
“There are less controls over the streaming, so you could argue in some ways it’s worse,” than a native app, said Patel. Developers are also locked into using the video codecs provided in Safari on iOS, whereas they could use alternatives that might be better at handling latency inside a native iOS app.
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/19206401/akrales_190914_3666_0259.jpg)
All of this is compounded by yet another Apple policy: no third party browser engines. You can install apps like Chrome, Firefox, Brave, DuckDuckGo, and others on the iPhone — but fundamentally they’re all just skins on top of Apple’s Webkit engine. That means that Apple’s decisions on what web features to support on Safari are final. If Apple were to find a way to be comfortable letting competing web browsers run their own browser engines, a lot of this tension would dissipate.
As it relates to Epic v. Apple, a lot of this PWA discussion isn’t germane to the fundamental arguments in the case. Fortnite as a PWA would necessarily be a streaming app instead of a native game and that introduces an entirely different set of compromises. Which is why it’s so fascinating to see Apple’s lawyers float web apps as a potential solution — because web apps on the iPhone are famously more limited than they are on other platforms, including even Apple’s macOS.
The human-readable versus machine-readable code bit is back now — Grant is talking about how web apps don’t go through the same kind of compilation process that increases processing efficiency, yet another reason they’re not as good as native apps.
— Adi Robertson (@thedextriarchy) May 5, 2021
Even if every single browser feature was available on mobile Safari or even if Apple allowed alternative browser engines on the iPhone, a web app will never match the performance of a native app. At the end of the day, though, all the discussion of web apps in the Epic v. Apple case highlight the limitations of Apple’s App Store policies, not PWAs.