As soon as Martin Sharp opened the file, he knew the ice had been singing all summer.
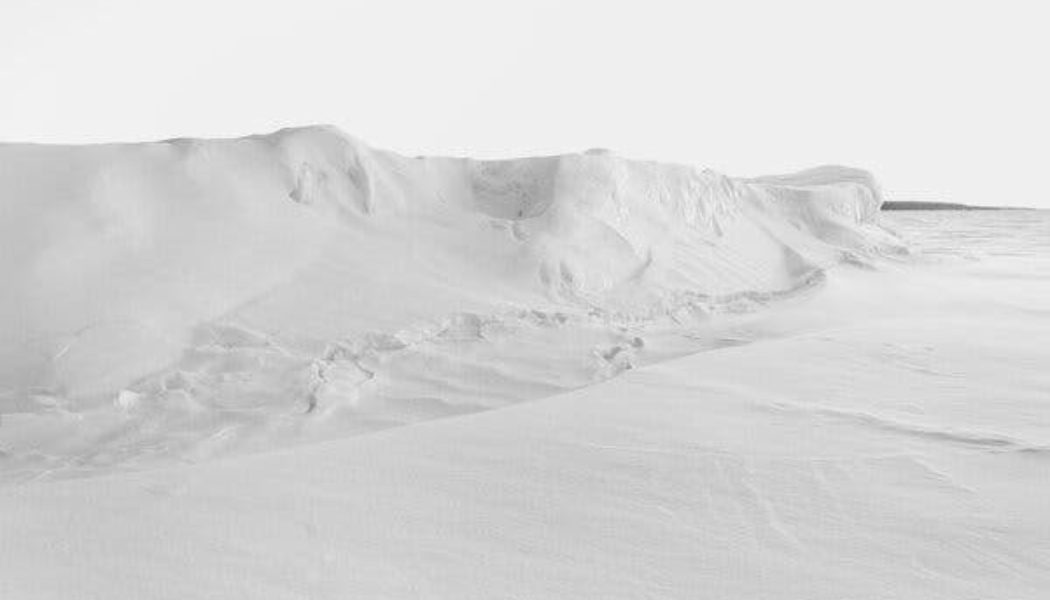
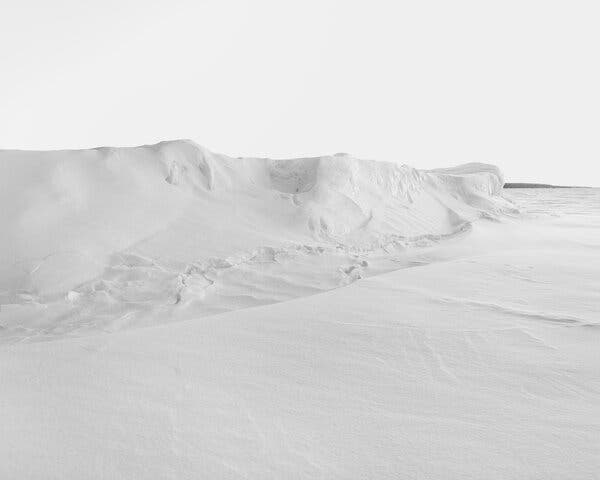
Several months earlier, Sharp — at that point, in 2009, a glaciologist at the University of Alberta for nearly two decades — had burrowed a cache of microphones into the Devon Ice Cap, a frozen mass in far northern Canada the size of Connecticut. Seven large microphones and GPS sensors monitored the rate of the melting ice atop the cap, while several seismic monitors sensed how the ice moved along the Earth, too. Almost as an afterthought, Sharp set up a little Sony hand-held recorder, hoping it might capture the essence of the frigid stillness where he often worked.
The result teemed with surprises: A snow bunting perched on the rig and sang. Gulls circled above. And below, as deep ice gradually thawed, an unexpected symphony unspooled. Water trickled past the microphone, creating a vertiginous drone, while tiny bubbles — air trapped inside the ice, perhaps for centuries — exploded incessantly, creating an allegro of snaps and pops that conjured the electronic productions of Autechre and Aphex Twin. Sharp began playing a 20-minute tape during lectures. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change asked for a copy, hoping to add sonic context to dry discussions about data and policy.
“It gave people a different way into what I was talking about, other than just showing slides,” Sharp, 64, said with a chuckle by phone. “The sound conveyed what it was like to be there.”

In recent years, the assorted and unexpected sounds of ice have periodically gone viral — the laserlike phenomenon of someone skating across thin ice, the shootout sensation of ice being dropped into a frozen hole, the meditative sighs of ice forming and popping inside a Swedish lake. But several scientists and musicians believe it all could have power beyond being mere online curios. Recordings of melting ice, splintering glaciers and cascading runoff could help predict the rate of climate change and sea-level rise; music made with such sounds, some hope, could lead listeners to rethink their relationship to nature. If more people can actually hear climate change through the once-unknown songs of failing ice, can they be inspired to help prevent it?
“I’m privileged that I can go somewhere and study these glaciers, but what about people who have to use their imaginations?” asked Grant Deane, 61, a longtime researcher at the University of California, San Diego.
Since 2009, he has plotted methods to use recordings of melting ice and calving glaciers — chunks splitting from the monolith’s edge above or below water — to document and predict the rate of loss and concomitant rise of sea levels. The planet is in a constant state of flux, of course, so melting ice and calving glaciers are natural processes, with changing seasons or epochs. But the glaciers Deane studies are receding at a rapid rate he attributes to greenhouse gases, and he believes it’s possible to hear that acceleration. He aims to build 12 substations along Greenland’s coast to chart the attrition of the island’s gargantuan ice sheet through sound.
Such science, he warned, held only so much possible public sway. “When people like me start talking about melting ice, it seems so far-off and unconnected from our everyday lives,” continued Deane, who has contributed recordings to immersive installations by the Canadian artist Mia Feuer. “How can people care about that when they’re dealing with immediate problems? Music can make those connections.”
FOR NEARLY TWO decades, the Norwegian musician Jana Winderen has been at the forefront of transforming her straightforward recordings of glaciers and the land and water surrounding them into emotional records, poignant musical postcards from melting and cracking masses of ice. During a 2006 family vacation in Iceland, Winderen dipped a hydrophone — a sealed microphone that detects pressure changes underwater — under a glacier’s edge. She shushed her daughters, sloshing in nearby mud, so she could tease out the source of some plangent rumble.
“It sounded like a loud engine, so I started looking for a tractor,” Winderen, 57, said recently, speaking by video in her studio from her family’s farm outside Oslo. “But I realized for the first time that the glacier is gliding — really, really slowly — on this water underneath sediments. And the sound has presence, like a creature. I totally fell in love.”
A former aspiring marine biologist whose mother was an early member of the Norwegian environmental advocacy group Future in Our Hands, Winderen soon realized the transformative capabilities of such sounds. A photo of an iceberg, she recognized, was gorgeous; the brutal noise it made while breaking free from a glacier, however, could be harrowing. Even fusillades of tiny pops from escaping air proved evocative, as the frozen world gave way to heat. “People could close their eyes and be there with the ice, be present,” she said. “It wasn’t like I had just recorded something and brought it there.”
Every time Winderen wields a microphone, the sounds surprise her. She can hear differences between ice that’s old and young, inland or seaside. But she has never hoped to be a mere stenographer, simply playing back what she heard while suspended precariously in glacial crevasses or trying not to capsize off the coast of Greenland after icebergs hit the water. She processes raw recordings, turning them into extended collages. Her albums — particularly “Energy Field” from 2010, which occasionally calls to mind drum-less heavy metal or an untuned violin — unfurl as tone poems, giving her changing surroundings a spiritual gravitas.
“I am not archiving that sound or this sound — that’s not interesting to me,” Winderen said. “It’s more interesting to be out there and listen, to figure out what’s happening and have an awareness of how much we don’t know.”
For the veteran Australian sound artist and researcher Philip Samartzis, it took an unprecedented Antarctic blizzard to accept the political potential of ice’s songs. Samartzis first visited the continent, through an arts fellowship in 2010, to map the acoustic environment of the Davis research station, one of Australia’s three outposts there. How, he wondered, did existence sound at this end of the earth?
“I tried to render the experiences as authentically as possible,” Samartzis, 60, said by video during vacation in New Zealand. “So you have very detailed forensic recordings of the station — without wind, which I was very adept at removing.”
But, as Samartzis admitted with a grin, bowdlerizing wind from the breeziest place in the world wasn’t very authentic. When he returned in February 2016, he intended to focus on wind itself, to log the ways it pulverized the place. He got his chance, during the strongest summertime blizzard ever witnessed there. As ice and snow pelted eight microphone stations through the 36-hour storm, the timbre of his work began shifting.
Though Samartzis often talked with wonder about the way the Antarctic ice would “sing,” how dynamic and curious it always seemed, the roar he’d chronicled was terrifying, a bewildering testament to climate change’s ferocity. His “Atmospheres and Disturbances,” out in March, fastidiously presents the sounds of melting permafrost, contracting glaciers and human activity that seems to exacerbate both at a research outpost more than two miles above sea level in the Swiss Alps. Hearing the disappearance is haunting and hair-raising, like watching a television show about hunting ghosts.
“When I talk to scientists about climate change, everyone’s all talked out. Essentially everyone knows, so it’s, ‘Why should I listen to you and your report?’” Samartzis said. “These recordings may not be scientifically sound, but it’s a whole other way of communicating knowledge, a different aperture of experience.”
Still, at least one pioneer of portraying ice through music worries that all this work arrives too late — and that simply capturing these songs of surrender and playing them back through loudspeakers can never get to ice’s might or grandeur. More than three decades ago, the young German producer Thomas Köner sat at the foot of a Norwegian glacier and marveled as fog rose and fell above it, like enormous frozen lungs breathing deliberately.
Between 1990 and 1993, Köner, who uses they/them pronouns, funneled such observations into a trilogy of lauded ambient albums that steadily evoked the awe and unease of being surrounded by ice that loomed, moved and cracked. But Köner believes that “Novaya Zemlya” — their 2012 album inspired in part by the glaciers of the Arctic archipelago of the same name — may be their final ice work. The Soviet Union tested the largest-ever atomic bomb there in 1961; for Köner, it represents humanity’s true relationship to nature.
“This was the end of, if not the love affair, the loved object — the idea of this pristine world of ice,” Köner, 57, said by phone from an artist residency in Serbia. “It is very sad, like you lost somebody. But you keep going on.”
Such presiding melancholy has motivated Eliza Bozek, 30, and a cadre of other young musicians to get to glaciers now, not later. An acolyte of the emotionally textured work of Winderen and Chris Watson (a prolific sound artist partly responsible for David Attenborough’s “Frozen Planet”), Bozek thinks that allowing people to hear ice creates an opportunity for awareness and, just maybe, altered behavior.
“They’re beautiful, but there’s a slow violence to the sounds, too,” said Bozek, who makes music under the name moltamole, from her Copenhagen apartment. “The sounds are political statements that are not available to our ears unless they’re recorded. They create space for empathy.”
LATE LAST YEAR, Sharp’s 2009 recording atop the Devon Ice Cap, the one he played during lectures, enjoyed an unexpected reprise on an album called, simply, “Ice Records.” The London artist and filmmaker Susan Schuppli first encountered Sharp while making a documentary about the Canadian Ice Core Lab, where more than 1,300 samples pulled from glaciers shape a portrait of Earth’s climate history. He was the archive’s first director.
Schuppli wove a portion of Sharp’s file into a 24-minute collage of ice recordings she and other researchers had made around the world by climbing into crevasses or sticking hydrophones beneath a glacier’s watery lips. The snippets are loud and vibrant, almost ecstatic, an atmosphere of ice offered with an exclamation mark. “I didn’t want to treat it as a mute witness,” Schuppli said by video from her home in London. “That sound gives us access to its change almost in real-time.”
Toward the middle of “Ice Records,” as meltwater gurgles beneath India’s enormous Drang-Drung Glacier, several women laugh. In the village of Akshow, they’d depended on that water their entire lives; as the melting accelerates, however, they may be threatened by “outburst floods,” when the water overruns whatever reservoir previously held it. But these women had never visited Drang-Drung, let alone listened to it. Schuppli led them up the ice and handed them headphones, so they might hear it morph beneath their feet.
“It was not about mourning this glacier but trying to understand what was going on,” Schuppli said. “How does science produce hospitality, so it’s not just scientists saying why their work is important? These women were enthralled. They didn’t want to stop listening.”