MSF
Misinformation About COVID-19 Can Be Devastating in Rural West Africa
Sierra Leone was later than most to experience its first cases of COVID-19. Though the virus itself did not arrive in the country until 31 March 2020, rumours and fears spread among communities well before the country’s first confirmed case. As happened during the Ebola outbreak from 2014-2016, this pandemic has led to rumours and misinformation that leave some people fearful of visiting healthcare facilities. This could have a devastating effect on children as, at 105 deaths per 1,000 live births, Sierra Leone has one of the highest rates of child mortality in the world. Memories of Ebola mean adopting new hygiene measures to reduce the spread of a pandemic is nothing new for people in Sierra Leone. However, as during Ebola, rumours can spread easily and this can lead to a ...
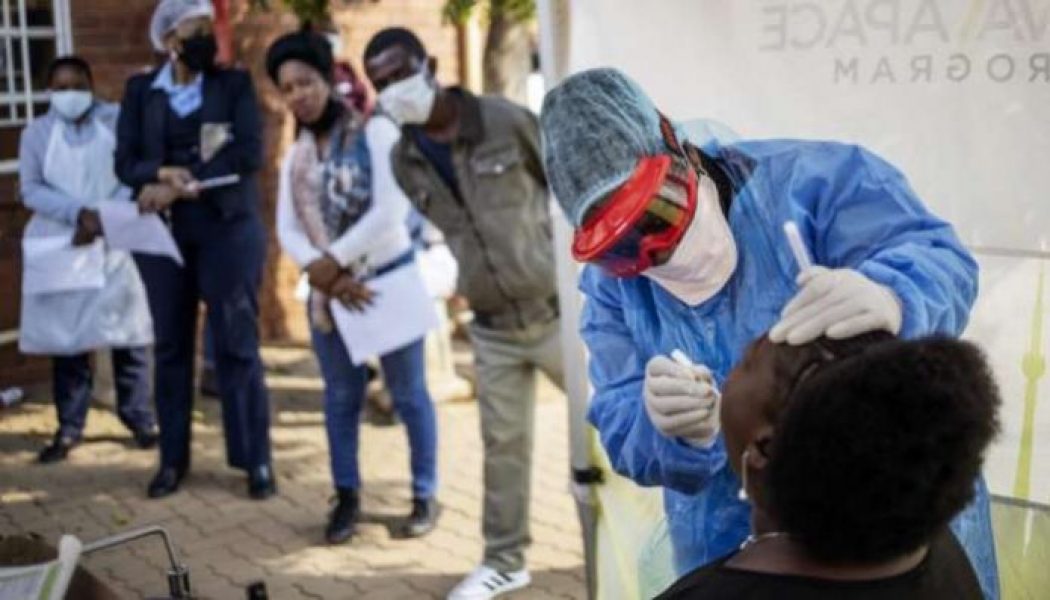
South Africa’s mass testing hits limits as virus spreads
With an expert flick of the wrist, South African nurse Bhelekazi Mdlalose collected throat swabs from young men lining up for coronavirus testing at a run-down hostel in downtown Johannesburg. Health workers were sent to the overcrowded block of single-room flats — mainly occupied by men from rural areas doing odd jobs in the city — as part of a mass community screening and testing (CST) campaign launched by the government last month. Mdlalose, who is employed by Doctors Without Borders (MSF), left her family and usual job in the northwestern town of Rustenberg in March to support community work in Johannesburg. Aged 51, she trains government health workers to handle suspected coronavirus patients correctly, checking in on CST teams deployed to townships, offices and shopping malls. “We id...