Cybersecurity South Africa
What is POPIA and What Does it Mean for Cybersecurity
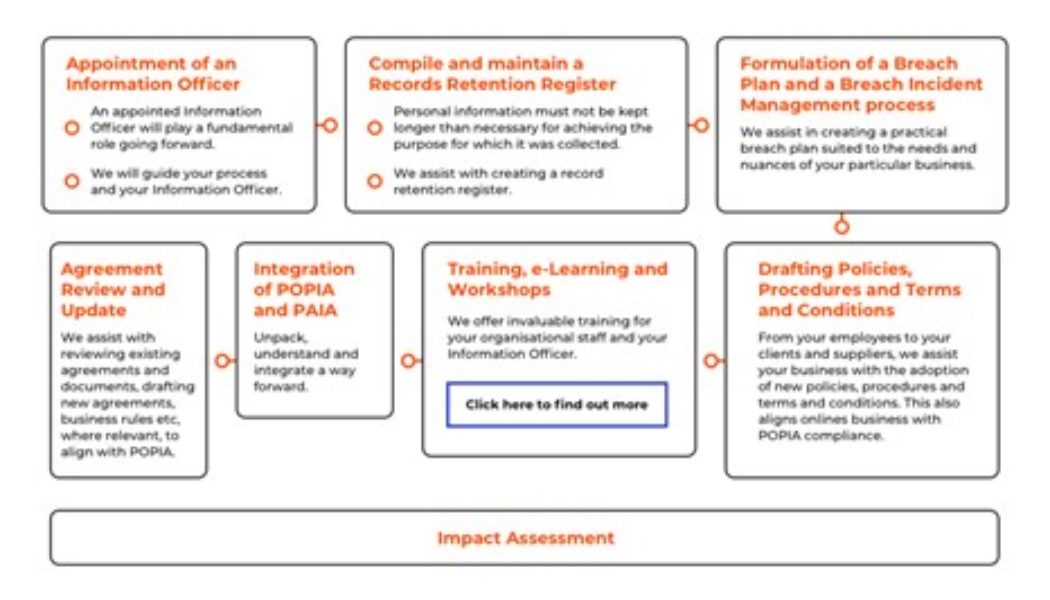
With an inundation of information from all angles regarding The Protection of Personal Information Act (POPIA), and the 1 July commencement date quickly approaching, organisations could be forgiven for feeling more than a little overwhelmed. Emmanuel Tzingakis, Technical Lead for Trend Micro Sub-Saharan Africa, contemplates how POPIA can assist organisations to secure their data and be better enabled to handle any potential cyber threats. What is POPIA? With personal information becoming a hot commodity on the dark web it is critical to understand exactly how to protect data from cybercriminals. A recent global survey revealed that 79% of organisations experienced disruptions, financial loss or other setbacks due to a lack of cyber preparedness in 2020. As work from home strateg...
South African Organisations Lag Behind Global Average of Cybersecurity Resilience
Email and data security company, Mimecast, unveiled its fourth-annual State of Email Security 2020 report. This report summarises details from 1,025 global IT decision-makers on the current state of cybersecurity. The findings in this year’s report demonstrate that despite high levels of confidence in respondents’ cyber resilience strategies, there is a clear need for improvement. While a large majority (77%) of respondents say they have or are actively rolling out a cyber resilience strategy, only 62% of South African organisations are doing the same. Yet an astounding 47% of local organisations – and 60% of global ones – believe it is inevitable or likely they will suffer from an email-borne attack in the coming year. South African respondents cite data loss (35%), a decrease in employee...
Web Skimming – A New Way to Steal Payments from Online Shoppers
Sourced from IOL. Researchers from cybersecurity and antivirus experts, Kaspersky, have uncovered a new technique for stealing users’ payment information on online shopping websites – a type of attack known as web skimming. Web skimming is a popular practice used by attackers to steal users’ credit card details from the payment pages of online stores, whereby attackers inject pieces of code into the source code of the website. This malicious code then collects the data inputted by visitors to the site (i.e. payment account logins or credit card numbers) and sends the harvested data to the address specified by attackers. Often, to conceal the fact that the webpage has been compromised, attackers register domains with names that resemble popular web analytics services, such as Google Analyti...