cybercrime
Cybercrooks to ditch BTC as regulation and tracking improves: Kaspersky
Bitcoin (BTC) is forecasted to be a less enticing payment choice by cybercriminals as regulations and tracking technologies improve, thwarting their ability to safely move funds. Cybersecurity firm Kaspersky in a Nov. 22 report noted that ransomware negotiations and payments would rely less on Bitcoin as a transfer of value as an increase in digital asset regulations and tracking technologies will force cybercriminals to rotate away from Bitcoin and into other methods. As reported by Cointelegraph, ransomware payments using crypto topped $600 million in 2021 and some of the biggest heists such as the Colonial Pipeline attack demanded BTC as a ransom. Kaspersky also noted that crypto scams have increased along with the greater adoption of digital assets. However, it said that people have be...
Interpol reportedly creates dedicated unit to fight crypto crimes
The International Criminal Police Organization is reportedly planning to strengthen its crackdown on cryptocurrency-related crimes by forming a dedicated division. Interpol, the world’s largest global police organization, has set up a special team in Singapore to help governments fight crimes involving virtual assets, the Indian news agency Business Standard reported on Oct. 17. Interpol made the announcement at a press conference ahead of its 90th general assembly in Delhi, which is to be attended by high-profile police officials from its 195 members from Oct. 18 until Oct. 21. According to Interpol secretary general Jürgen Stock, the absence of a legal framework for cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ether (ETH) poses major challenges to law enforcement agencies. “Because very often...
How AI & Machine Learning Can Provide Defense Against Cybercrime
Nowadays, threat actors are leaning on new tools and techniques to improve the efficiency of their attacks. Only artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning move quickly enough to defend organisations in this evolving cyber threat landscape. “In the past three months, we’ve been seeing more speed and speed can kill,” says Derek Manky, Chief Security Strategist & VP Global Threat Intelligence at FortiGuard Labs. Threats have been getting into a system, hitting the targets, exfiltrating data, demanding ransom, and getting out of a system, much quicker than normal. This includes attackers capitalizing on new vulnerabilities, zero-days and n-days. They also appear to have become more aggressive, with double extortion, triple extortion and targeted attacks. “Their approaches are more ...
Blockchain audits: The steps to ensure a network is secure
The last few years have seen blockchain platforms becoming the centerpiece of many tech conversations across the globe. This is because the technology not only lies at the heart of almost all cryptocurrencies in existence today but also supports a range of independent applications. In this regard, it should be noted that the use of blockchain has permeated into a host of novel sectors, including banking, finance, supply chain management, healthcare and gaming, among many others. As a result of this growing popularity, discussions pertaining to blockchain audits have increased considerably, and rightly so. While blockchains allow for decentralized peer-to-peer transactions between individuals and companies, they are not immune to issues of hacking and third-party infiltration. Just a ...
Update Your Security Strategy Based on Key Information Learned About Threat Actors, Advises Netskope
The reality of the cyber threats posed today is that many threat actors are not rogue operators acting on their own but are, instead, working as part of sophisticated and organised groups, collaborating with other groups within a wider ecosystem of specialists. These groups build significant financial resources over time, derived from the proceeds of commercially-driven attacks, or gathered as payment from states sponsoring or directly commissioning their activities. This is according to Yaroslav Rosomakho, Field CTO of Netskope, a global cybersecurity leader which is redefining cloud, data, and network security to help organisations apply Zero Trust principles to protect data. He explains: “Threat actors use these resources to improve their subsequent attacks, paying for infrastructure or...
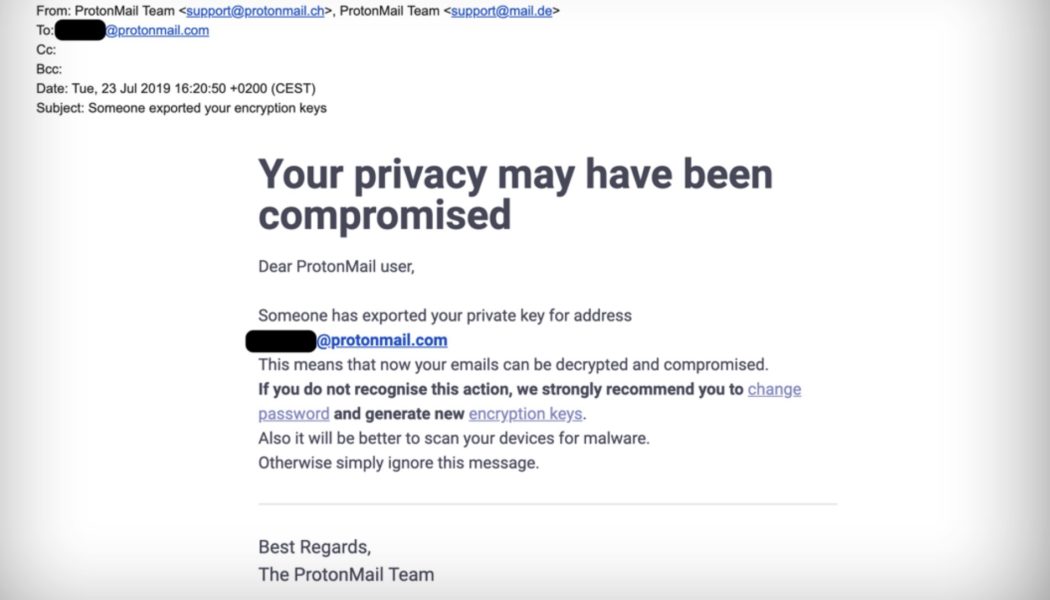
The Great Phishing Fail
Anna Collard, SVP Content Strategy & Evangelist at KnowBe4 Africa. In 2021, phishing attacks increased by 7.3% according to the ESET Threat Report, and the Cisco 2021 Cybersecurity threat trends report revealed that around 86% of organisations had at least one person click a phishing link. This echoes the findings of recent KnowBe4 Security Awareness Research that found people keep clicking – on fake emails from HR, the business and IT. As Anna Collard, SVP Content Strategy & Evangelist at KnowBe4 Africa, points out, the majority of top email categories that people fall for are those that fit in to everyday life – invoices, purchase orders, shared files, and COVID-19 related topics. “As our quarterly report on the top-clicked phishing tests shows, the emails that catch people are t...