cyber attacks
UK: Some countries are using coronavirus vaccines as a geopolitical tool
British foreign minister Dominic Raab said on Friday there was no doubt some countries were using vaccines as a diplomatic tool to secure influence but Britain did not support so-called vaccine diplomacy. Raab was speaking to Reuters on the sidelines of a G7 summit in Cornwall, southwestern England, that was likely to be dominated by the West’s attempts to reassert its influence as the world looks to rebuild from the COVID-19 pandemic. Western diplomats fear Russia and China are using their vaccines to gain influence across the world, especially in poorer countries that do not have their own production or the means to buy shots on the international market. Asked whether he was concerned that China and Russia could use vaccines in exchange for influence, Raab said: “There’s no doubt there’s...
Why Cyber Attacks are Technology’s ‘Natural’ Disasters
Sourced from Forbes The SolarWinds attack was stunning in its scope and scale. If it were an earthquake, it would be 9.9 on the Richter scale. As digital transformation accelerates in 2021 and beyond—and applications accelerate as central enablers of business and all manner of digital life—cyberattacks have become technology’s natural disasters. Both have the power for profound devastation, threaten our sense of safety, and are (sadly) the reality of our world today. There is, however, one notable difference between a natural disaster and cybercrime. It is within our control to reduce the devastating impact of cybercrime. We can learn from the weaknesses the SolarWinds attack exposed and use this event as a catalyst for behaviour changes that will materially reduce the impact of future att...
Opportunities & Risks From the 4th Industrial Revolution in Africa
Sourced from Shutterstock. Insurance provider and risk mitigator Aoncyber has published a new report titled “Cyber Risks in Africa.” The report focuses on the 4th Industrial Revolution (4IR) which is ushering in a new economy and a new form of globalisation, both of which demand new forms of governance to safeguard the public good. This new chapter in human development is enabled by extraordinary technological advancements, and along with this progress comes inherent risks. African states need to equip themselves better when it comes to cyber resilience in order to actively participate in the global economy, by effectively managing and mitigating the effects of data breaches and cybercrime on their economy and citizens. The 4th Industrial Revolution brings many opportunities, as well as in...
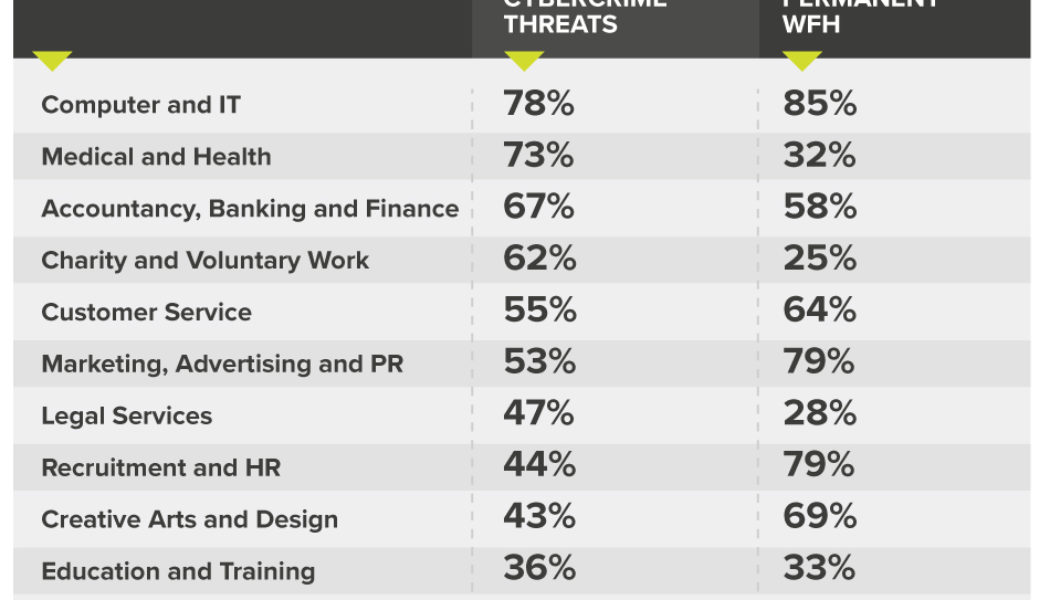
Cybercrime has Increased by 33%, Report Shows
The 100 Days of Coronavirus report – published by Mimecast – shows that the volume of malicious and opportunistic cybercrime has increased significantly by 33% in the period January to March 2020. The new report has found that in the period January to March 2020 monthly volumes of: Spam and opportunistic cybercrime detections increased by 26.3%, Impersonation fraud detections increased by 30.3%, Malware detections increased by 35.16%, and Blocking of URL clicks increased by 55.8%, meaning people are more likely now to click on unsafe links than before the outbreak. Over the months of February and March, as South Africa reported its first case and moved swiftly into lockdown, the Threat Intelligence Team saw dramatic increases in cyberattacks in Sub-Saharan Africa. Carl Wearn, Head of E-Cri...
- 1
- 2