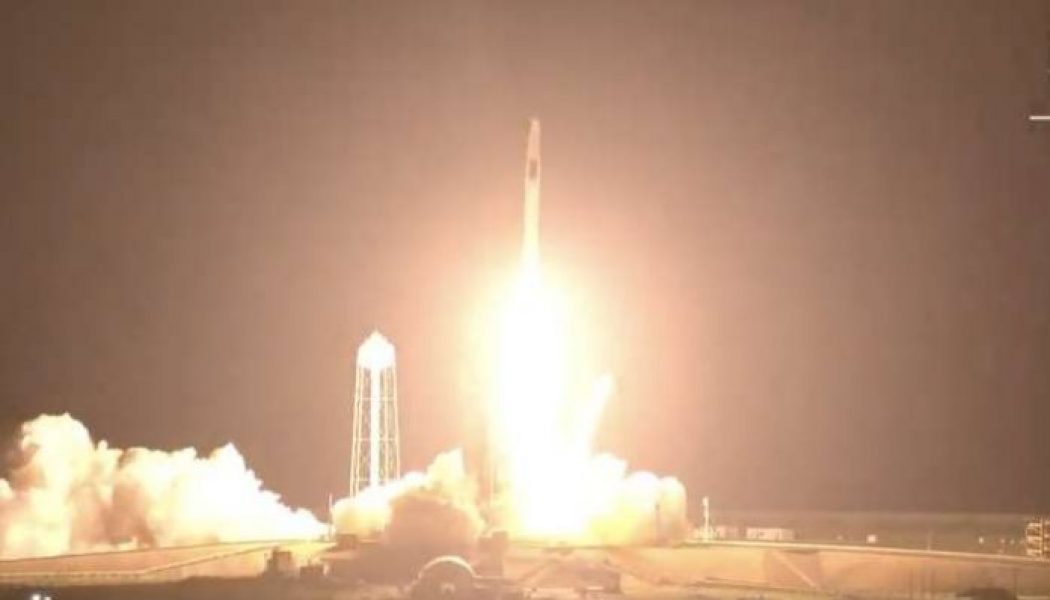
SpaceX launched its third crew of astronauts to the International Space Station early Friday morning, reusing a Crew Dragon space capsule to fly humans for the first time. The mission, dubbed Crew-2, is the latest flight under NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, and will add four more astronauts to the orbital space station.
A used Falcon 9 rocket, last flown for SpaceX’s Crew-1 mission last year, lifted off at 5:49AM ET from Cape Canaveral, Florida carrying Endeavor, the same Crew Dragon capsule that first launched SpaceX’s debut astronaut mission nearly one year ago. For this flight, the Endeavor capsule carried four astronauts from three different countries — SpaceX’s most diverse NASA-managed crew yet.
“Off the Earth, for the Earth, Endeavor is ready to go,” NASA astronaut Shane Kimbrough, the mission’s spacecraft commander, told SpaceX mission control in Hawthorne, California minutes before lifting off.
3.. 2.. 1.. and liftoff! Endeavour launches once again. Four astronauts from three countries on Crew-2, now making their way to the one and only @Space_Station: pic.twitter.com/WDAl8g7bUK
— NASA (@NASA) April 23, 2021
Kimbrough and fellow NASA astronaut Megan McArthur, serving as the pilot, accompanied mission specialists Akihiko Hoshide of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and Thomas Pesquet, a French aerospace engineer from the European Space Agency (ESA). The crew will spend roughly 23 hours in transit as Endeavor autonomously raises its orbit toward the ISS ahead of a 5:10AM ET docking tomorrow, April 24th.
Kimbrough, McArthur, Hoshide and Pesquet will spend six months in space and join seven astronauts already aboard the space station, an orbital science laboratory flying more than 17,000 miles per hour in orbit roughly 250 miles above Earth. Two days after the crew’s arrival, four other astronauts from SpaceX’s Crew-1 mission, which launched to the ISS November 15 last year, will board a separate Crew Dragon capsule and return to Earth to cap their own six-month stay.
Crew-2 marks SpaceX’s third astronaut mission under NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, the agency’s public-private initiative to revive its human spaceflight capabilities after a nearly 10-year dependence on Russian rockets. It’s the second of six operational missions SpaceX is contracted to fly under that program, which awarded the company $2.6 billion in 2014 to develop and fly Crew Dragon. SpaceX’s first crewed mission in May 2020, carrying Bob Behnken and Doug Hurley, counted as a test flight.
Accompanied by two Russian cosmonauts and NASA’s Mark Vande Hei, who all launched on a Russian Soyuz rocket on April 9th, Crew-2’s stay aboard the ISS will make for an 7-person crew in space for the next several months. During their stay, the crew will conduct an array of microgravity science experiments. The Crew-2 astronauts’ science efforts will center on a cassette-sized device containing human cells to study how those cells respond to various drugs and health conditions in microgravity.
The increased crew size means other science experiments, including a few projects tracking how plants grow and behave in space, will also see some progress. “It’s like a party up there,” said Annmarie Eldering, a project scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory working on Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3, a device astronauts will use to measure carbon dioxide in Earth’s atmosphere. “When you get all those measurements from space, in the same time, same place, it’s really powerful for science,” Eldering said Friday morning in a live NASA broadcast.