I’d love to know how many wheels are curbed and bumpers are tapped each year in attempts to parallel park. There’s a whole industry of rubber bumper guards built around how difficult parking alongside a curb can be; crowded cities like New York are full of them.
You might catch yourself thinking, “If cars can sort of drive themselves, why can’t they sort of park themselves?” They can.
How Does Self-Parking Work?
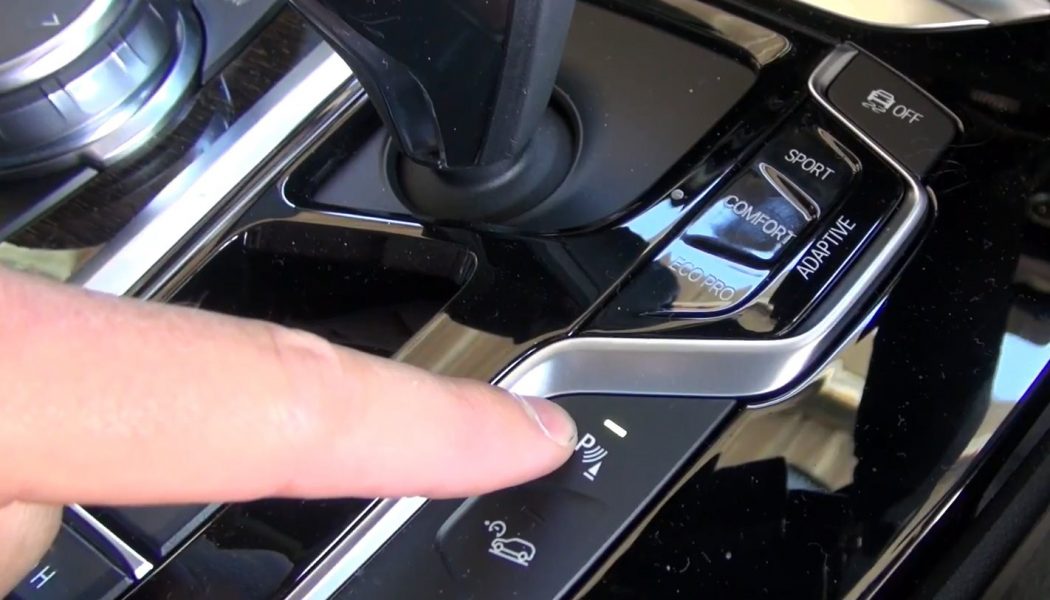
Most cars with self-parking capability can’t actually do it all themselves. These systems can locate a parallel (and in some cases a perpendicular or diagonal) parking spot upon activation by utilizing proximity sensors on the front, side, and rear of the vehicle; often, the tech requires activating a turn signal to indicate what side of the road it should look for a space. Once the spot has been located and the driver has selected it and come to a stop, the vehicle will issue instructions to shift into the proper gear.
The automated aspect of things is the steering. Once the driver shifts into reverse, they will operate the gas and brake as the car steers itself into the parking space. (Some self-parking systems will handle acceleration and braking on your behalf.) The proximity sensors will issue an alert if the car is at risk of colliding with an obstacle, and if necessary, the car will ask that you shift back into drive to finish the parking maneuver. The vehicle will also provide steering assistance for leaving the spot.
Those are the basics, but some systems boast additional functionality. Available remote park assist systems in the BMW 7 Series and Hyundai Sonata (remember Smaht Pahk?) enable you to pull the car into or out of a tight parking space via controls on the key fob. Tesla takes it a step further with Smart Summon, which can autonomously guide your car out of a parking space and to your location, as long as you’re less than 200 feet away.
Different names for self-parking tech
- Parking Assistant Plus (BMW)
- Automatic Parking Assist (Chevrolet, Mercedes-Benz, Ford, Cadillac, Buick, GMC)
- Park Assist (Volkswagen, Jaguar, Land Rover, Audi)
- Autopark (Tesla)
- Park Assist Pilot (Volvo)
- ParkSense Active Park Assist (Ram, Alfa Romeo, Jeep, Chrysler)
- Active Park Assist (Lincoln)
- Intelligent Parking Assist (Toyota)
The post Self-Parking Cars Explained: How Does Automatic Park Assist Work? appeared first on MotorTrend.