Until now, Hyundai Motor Group has focused on fitting electric powertrains into vehicles that were originally built to accommodate internal combustion engines. From the Hyundai Kona Electric to the Kia Niro EV, the automaker has started to achieve some success in this area, in spite of the compromises inherent to the approach. Now, it’s turning the page by introducing its first dedicated platform for battery electric vehicles. The platform will underpin a wide range of new electric models, with the first ones launching next year.
Dubbed E-GMP, the platform will underpin the Ioniq 5, a midsize crossover coming in early 2021. It will also be the basis for Kia’s first dedicated electric vehicle that will debut sometime next year. The platform will then expand across most vehicle segments, even big SUVs, offering various levels of performance. A future high-performance model on the platform will reach 62 mph in less than 3.5 seconds and achieve a top speed of 161 mph. Hyundai says to expect up to around 600 hp from the platform.
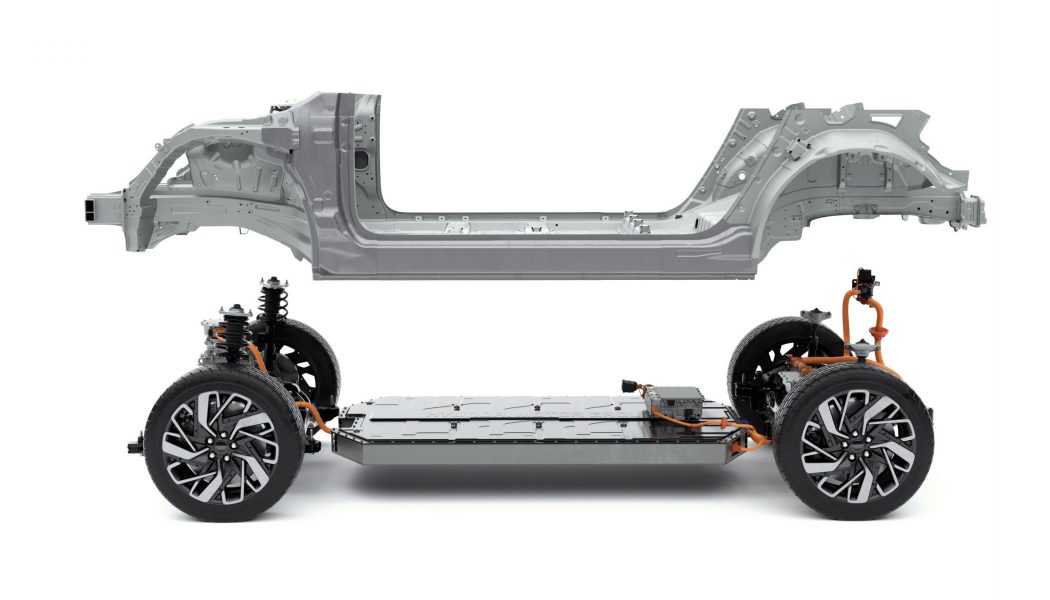
The new electric motor is smaller and has a maximum speed that’s 70 percent higher than existing motors. It’s one part of the platform’s new compact power electric system that combines the motor, transmission, and inverter into a single unit.
While the automaker has traditionally opted for front-wheel-drive EVs, the new platform relies on the rear wheels for propulsion in its most basic form. E-GMP can accommodate both rear-wheel and all-wheel drive, however, and vehicles with the latter configuration have an additional motor. (This is similar to the modular, reconfigurable nature of Volkswagen’s ID-branded EVs and its new MEB electric car platform, which can support a variety of drive configurations.) To improve ride comfort, Hyundai is using the first mass-produced integrated drive axle, which combines the wheel bearings with the drive shaft to power the wheels.
Drivers can recharge with either a 400- or 800-volt system. Hyundai says it has patented the technology compelling the motor and inverter to boost 400 volts to 800 volts for stable charging compatibility. It takes just 18 minutes to recharge the battery up to 80 percent with high-speed charging. The platform enables two-directional charging, meaning that the vehicle’s battery not only receives power from an external source, but can charge another EV or device without the need for extra components. Providing up to 3.5 kilowatts of power, it can run a mid-size air conditioner and a 55-inch television for up to 24 hours, Hyundai says.
It doesn’t mean much for those of us on this side of the Atlantic, but vehicles will have a maximum range of over 500 km (310 miles) on the European test cycle. This estimate isn’t comparable to range estimates for the EPA cycle, as they’re often fairly optimistic.
Eventually, the platform will be used on Genesis vehicles. Hyundai is also studying the platform’s application for fuel cell electric models. As to whether Hyundai will share the platform with other companies, the Korean automaker says there’s nothing to announce at this time, but there could be collaborations in the future.
If you’re a fan of the Kona Electric and Niro EV, know that the automaker isn’t giving up on EVs based on existing vehicle platforms. By 2025, Hyundai Motor Group will bring out 23 battery electric vehicles, 11 of which will be dedicated BEVs. The automaker aims to sell more than 1 million EVs around the globe by this time. Part of this strategy will involve its new Ioniq brand of electric vehicles, which will include the Ioniq 5, 6, and 7 vehicles to debut by 2024.