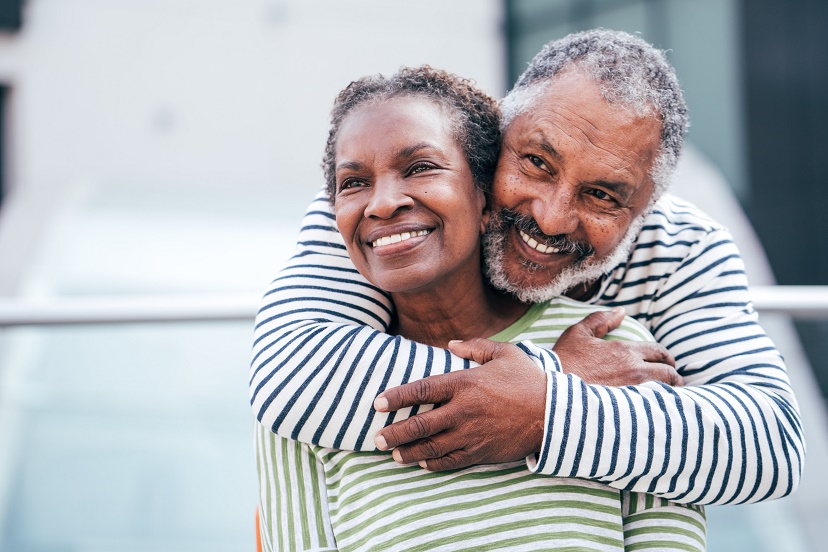
A lifestyle with a healthy diet and exercise is a great way of preventing the onset of diabetes.
Diabetes is a serious disease that affects millions of people in America. In fact, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports 40% of U.S. adults are likely to develop type 2 diabetes over their lifetime.
“There are many differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, said Dr. Branden Turner, a family practice physician with Kaiser Permanente Southern California, which is headquartered in Pasadena. “But in both types, blood sugar levels get too high. This increases the risk for complications, such as blindness and kidney failure. For both diseases, treatment focuses on keeping blood sugar levels within a target range to help prevent long-term complications.”
Brandon Landry, a Crenshaw District resident who has type 2 diabetes and is under the care of Dr. Turner, urged others to never take their health for granted, and live a lifestyle with a healthy diet and exercise to prevent the onset of diabetes.
Personally, Landry said he’s living a normal life now that he’s removed sugar from his diet, and is eating healthier food with no processed foods and a low amount of carbohydrates, all of which has helped him maintain a healthier weight and blood sugar level.
“Do the right thing and change your lifestyle to prevent diabetes before it’s too late,” he said.
What is diabetes?
Almost everything we eat is turned into glucose (sugar), which our body uses for energy. To help our body’s cells absorb glucose, an organ near the stomach – the pancreas – produces a hormone called insulin.
“When you have diabetes, your body either doesn’t make enough insulin, or can’t use its own insulin very well,” Dr. Turner said. “As a result, a build-up of glucose occurs in your blood, eventually leading to many health problems and complications.
For people with diabetes, research shows that:
• Blood pressure management can reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke by 12% to 27%, and the risk of progression of kidney disease by 30% to 70%.
• Cholesterol management can reduce cardiovascular complications by 20% to 50%.
• Regular eye exams and timely treatment could prevent up to 90% of diabetes-related blindness.
• Regular foot exams and patient education could prevent up to 85% of diabetes-related amputations.
• Prevalence: In 2019, 37.3 million Americans, or 11.3% of the population, had diabetes, both type 1 and 2.
• Nearly 1.9 million Americans have type 1 diabetes, including about 244,000 children and adolescents.
Tips to help you better manage your blood sugar:
• Have regular eating patterns. Eating the same number of meals around the same time each day helps control blood sugar.
• Eat many different foods. Eating from all food groups is an effective way to stay healthy.
• Limit fats. Eat foods that are low in saturated and trans fats, as well as cholesterol.
• Make room for fiber. High-fiber foods keep people fuller for longer. Whole-grain breads, vegetables, dried beans and fruits are all great sources of fiber.
• Watch your refined carbohydrates, including sugar. Starches and sugars raise blood sugar levels. Limiting these foods prevents blood sugar from going up.
• Exercise helps control blood sugar levels. It’s a good idea to exercise for at least 30 minutes a day. Walking, swimming and cycling are all great options. Consult your doctor before starting any exercise regimen.
• Exercise also helps you keep a healthy weight. This is important because excess weight makes the kidneys work harder and it also makes it hard to manage blood sugar.
Kaiser Permanente offers important information about diabetes.